Non-Destructive Testing Methods
If you have a component that you need to see internally or fully understand without destroying it then Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) may be what you are looking for.
 Ultrasound is a NDT method used to detect subsurface and surface flaws and discontinuities in many materials such as steel, carbon composites, castings, ceramics and plastics etc. The dimensions and locations of these flaws can be accurately determined to enable local repairs to be carried out. Accurate thickness measurement can also be easily obtained as used in corrosion surveys of tanks, pipework, ship structures etc.
Ultrasound is a NDT method used to detect subsurface and surface flaws and discontinuities in many materials such as steel, carbon composites, castings, ceramics and plastics etc. The dimensions and locations of these flaws can be accurately determined to enable local repairs to be carried out. Accurate thickness measurement can also be easily obtained as used in corrosion surveys of tanks, pipework, ship structures etc.
 Magnetic Particle Inspection is an NDT method used for locating surface and in some situations sub-surface flaws or discontinuities in a ferromagnetic material. Using permanent or electro magnets with white contrast paint, in conjunction with ferromagnetic iron filings suspended in a solution as a detection media, is the most common method of site inspection. In certain circumstances fluorescent solutions are used with Ultra Violet (Black Light) where painting of contrast paint is undesirable. A Magnetic Powder system can also be used on hot surfaces.
Magnetic Particle Inspection is an NDT method used for locating surface and in some situations sub-surface flaws or discontinuities in a ferromagnetic material. Using permanent or electro magnets with white contrast paint, in conjunction with ferromagnetic iron filings suspended in a solution as a detection media, is the most common method of site inspection. In certain circumstances fluorescent solutions are used with Ultra Violet (Black Light) where painting of contrast paint is undesirable. A Magnetic Powder system can also be used on hot surfaces.
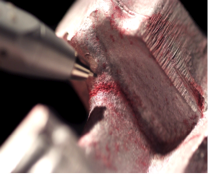 Dye Penetrant Inspection is an NDT method used for locating surface flaws and discontinuities in ferrous and non-ferrous materials including welds, castings and forgings using a dye and a developing powder. The method is based on using capillary action, where the dye solution used penetrates into surface-breaking flaws or discontinuity. The residual dye is then cleaned off and a developer powder is used which draws out the absorbed penerant leaving a visible trace for inspection. The on-site method is usually a colour contrast red dye but fluorescent dye can be used with Uv (Black Light); the latter method is mainly used in-house.
Dye Penetrant Inspection is an NDT method used for locating surface flaws and discontinuities in ferrous and non-ferrous materials including welds, castings and forgings using a dye and a developing powder. The method is based on using capillary action, where the dye solution used penetrates into surface-breaking flaws or discontinuity. The residual dye is then cleaned off and a developer powder is used which draws out the absorbed penerant leaving a visible trace for inspection. The on-site method is usually a colour contrast red dye but fluorescent dye can be used with Uv (Black Light); the latter method is mainly used in-house.
 Radiography is an NDT method used for locating cracks, inclusions and internal flaws/discontinuities in many materials using ionising radiations such as Gamma or X-Ray radiation. For site pipe weld examination the most commonly used is a Gamma isotope due to its portability. X-ray could also be used and would be the preferred option where better sensitivity and contrast of the resulting radiograph is required, allowing smaller flaws to be located or where thin materials are being tested. For radiography of larger structures such as valve castings or reinforced concrete bridges or flooring, then a portable high energy option of up to 7.5meV Betatron could be used.
Radiography is an NDT method used for locating cracks, inclusions and internal flaws/discontinuities in many materials using ionising radiations such as Gamma or X-Ray radiation. For site pipe weld examination the most commonly used is a Gamma isotope due to its portability. X-ray could also be used and would be the preferred option where better sensitivity and contrast of the resulting radiograph is required, allowing smaller flaws to be located or where thin materials are being tested. For radiography of larger structures such as valve castings or reinforced concrete bridges or flooring, then a portable high energy option of up to 7.5meV Betatron could be used.
 Thermography is a remote NDT method using an infrared camera checking for abnormalities be that hot or cold areas on a component or object when in operation. It can detect temperature differences of less than 0.25oC and images can be captured as a data file or recorded as a video. The technique can be used to detect thinning, corrosion/erosion on damaged plant; it can also be used to locate leaks and blockages as well as cracks in concrete, disponds and laminations in laminates.
Thermography is a remote NDT method using an infrared camera checking for abnormalities be that hot or cold areas on a component or object when in operation. It can detect temperature differences of less than 0.25oC and images can be captured as a data file or recorded as a video. The technique can be used to detect thinning, corrosion/erosion on damaged plant; it can also be used to locate leaks and blockages as well as cracks in concrete, disponds and laminations in laminates.